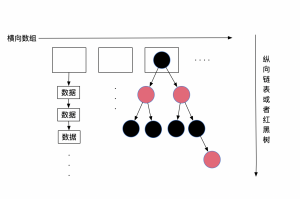
hashMap的数据结构
作者:binHashMap的数据结构:HashMap的数据结构为 数组+(链表或红黑树)
为什么采用这种结构来存储元素呢?
- 1.数组的特点:查询效率高,插入,删除效率低。
- 2.链表的特点:查询效率低,插入删除效率高。
在HashMap底层使用数组加(链表或红黑树)的结构完美的解决了数组和链表的问题,使得查询和插入,删除的效率都很高。
Object类有一个hashCode方法:
public native int hashCode();
思路就是:通过将hashCode均分到数组中,然后在数组中插入链表。
如图:
我们可以关注HashMap.putVal的这一段:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//懒加载,第一次put的时候,去吃初始化容量,或者容量不够了去扩容
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//节点为空,插入头节点
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
//头节点就找到了,大多数情况都可以头节点找到,hash冲突才会出现链表
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
//树结构的话,插入树
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
//链表结构遍历往后找
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
//链表中找不到新建节点
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//链表中找得到
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
//判断是否要做值的覆盖
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
//容量超过阈值进行扩容
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
默认数组容量是16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
什么时候将链表转为红黑树?
//链表长度大于8,就转红黑树
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
...
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
什么时候将红黑树转为链表?
当节点在2-6个当时候,可能会转换为链表,取决于树当结构,规定了特定结构会转,因为是红黑树是平衡的,所以可以确定一个范围
if (root == null || root.right == null ||
(rl = root.left) == null || rl.left == null) {
//根节点为空、根节点无右子节点、或者左节点为空、或者左子节点的左节点为空
tab[index] = first.untreeify(map); // too small
return;
}